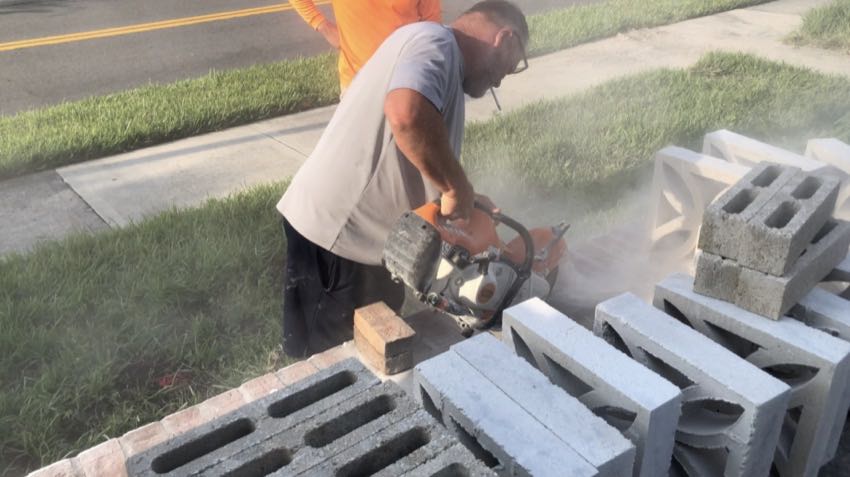
Few people really enjoy it when the government expands regulations. While there’s certainly been a lot of focus on silica dust regulation updates, we haven’t spent much time looking at the rationale behind it. Namely, the silicosis OSHA is trying to prevent construction Pros from suffering later in life. We go over just what is silicosis and also how it’s contracted. We also talk about silicosis treatment and what to do if you receive a diagnosis.
This article was updated with additional information on April 25, 2023.
All About Silicosis
What is Silicosis and What are the Symptoms?
Silicosis is lung fibrosis that takes hold when you breathe in silica dust. Concrete and masonry work, mining, and other sectors kick up this type of dust on a regular basis. As you breathe in silica dust, it damages the lining of your lungs’ air sacs. This creates eventual scar tissue inside your lungs and can cause fluid buildup, affecting your ability to breathe as your lungs stiffen.
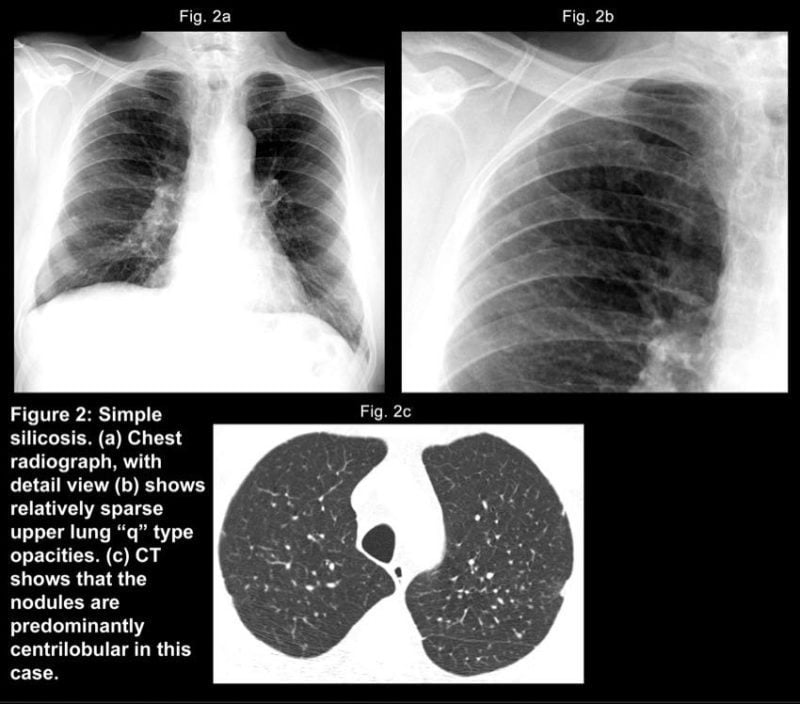
What Causes Silicosis?
To avoid it, you might want to know what causes silicosis and how it is contracted. Breathing in silica dust doesn’t automatically give you silicoses. Susceptibility and repeated contact do. Acute silicosis symptoms can begin as early as a few weeks after exposure and include a cough, weight loss, and fatigue. In some people, it may take years before the symptoms occur.
Chronic silicosis is typically contracted after 10 to 30 years of persistent exposure. This gets into your upper lungs and can result in extensive scarring.
If you remain in a high-exposure environment, you’ll experience accelerated silicosis. This could lead you to experience the long-term effects even sooner—usually within 10 years.
Can Silicosis Be Cured?
Disturbingly, no cure for silicosis exists, and it also increases your risk of lung cancer, tuberculosis, and COPD. Only preventative measures will keep your lungs healthy.
Reducing Risk on Site
Updated regulations from OSHA lower the permissible exposure level (PEL) from 250 micrograms per cubic meter to 50 micrograms. They created Table 1 to offer an easy-to-read guide for selecting the right tools, accessories, and dust collection systems to keep you in compliance.
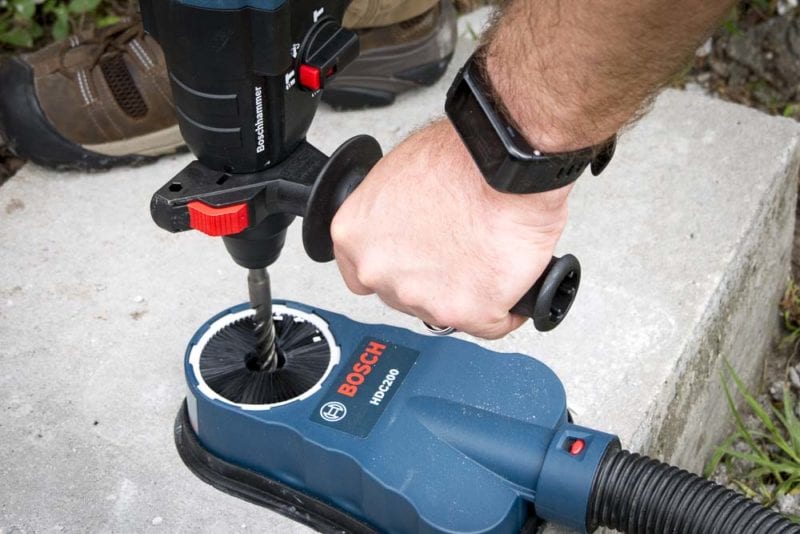

If you don’t see your application on the list, you can still use objective data to prove a system of tools and methods will keep you under the limit.
Finally, you can fit your crew with monitors to gather actual exposure data and ensure they stay below the limit.
Many tool manufacturers, like Bosch and Makita, make the process of selecting Table 1 compliant systems easier. These companies provide objective data documentation straight from their website. You can easily bring up the information in your job planning meeting, morning safety meeting, or access it on your smartphone.
Silicosis Statistics
- Around 2 million U.S. workers are exposed to silica in the workplace in the construction industry along with 300,000 workers in other industries.
- Silica dust, when it enters the lungs, causes inflammation. After prolonged exposure, this can develop scar tissue which makes breathing difficult.
- While no cure for silicosis exists, various treatments help alleviate symptoms.
- OSHA, workers, and employees can work together to follow guidelines and prevent silicosis.
- Silicosis can lead to additional problems like tuberculosis, lung cancer, chronic bronchitis, autoimmune disorders, and kidney disease.
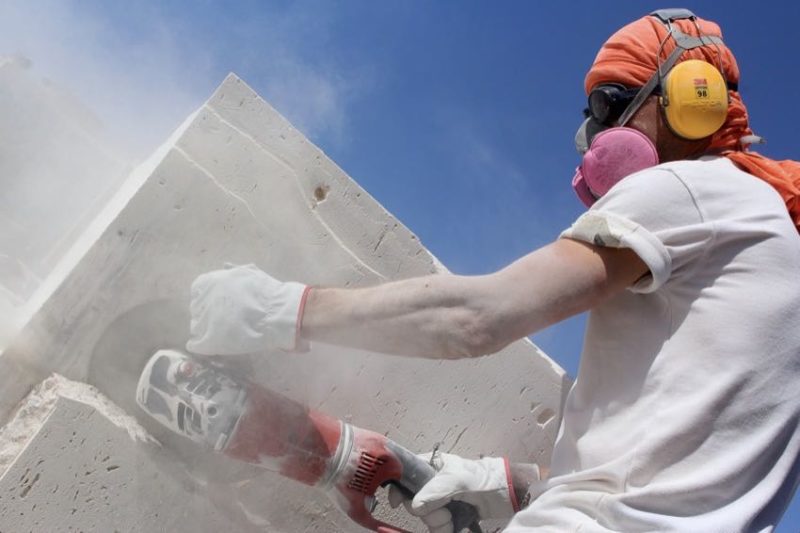

Additional Steps to Prevent Silicosis
If you work in a trade that has a risk of silica dust exposure, get proactive with your medical care. Your insurance likely carries a free or low-cost annual wellness exam. Let your doctor know you want to stay ahead of silicosis so he or she pays close attention to your lungs.
If think silicosis has already done some damage, they may want a lung CT scan, bronchoscopy, or biopsy. Some of this can help establish a baseline to continue monitoring your health. Either way, the upfront cost will be worth it if you’re able to prevent damage at a later date.
What is the Treatment for Silicosis?
Currently, the prevailing wisdom says there is no actual cure for silicosis. The damage silicosis does to your lungs is, unfortunately, irreversible. Most medical guidance centers around slowing the progression of the disease by avoiding further exposure to silica dust and beginning medical treatment.
If your doctor establishes that you have silicosis, it’s not the end of the world. The medical community has considerable experience in providing treatment for silicosis. Silicosis treatment does, however, involve some lifestyle changes. Obviously, you need to eliminate any additional exposure. You may also need to start using an inhaler to help decrease sputum and/or relax your air tubes.
If your silicosis is more advanced, your treatment may involve using oxygen on a regular basis. The most extreme cases may even see you put on the list for a lung transplant.
Once the disease sets in, you’ll have to avoid airborne irritants like smoke, pollen, and air pollution. Managing the disease takes a lot of care, and there’s no getting around the fact that it will be expensive.
How Long Can You Live With Silicosis?
As you might expect, the answer here is “it depends.” How long you can live with silicosis has much to do with the amount of exposure and duration of that exposure. The life expectancy of a person with silicosis really depends on the severity of the disease and the individual’s overall health.
As you probably know, some people can smoke cigarettes their entire lives and never get lung cancer while others get very sick very quickly. Silica dust differs because the particles or particulates are much larger than smoke, so they never truly leave your system.
In mild cases, a person with silicosis may live for many years without experiencing significant symptoms. However, in more severe cases, the life expectancy may be reduced, and the person may experience respiratory failure, lung cancer, or other complications.
Final Thoughts
We don’t want to scare anyone. The bottom line—what silicosis represents is a real concern. It needs to be addressed at the outset and for anyone who has had prolonged exposure or feels they may have contracted silicosis. As an employer, do your best to focus on prevention. This can help you alleviate or bypass most of these concerns.



